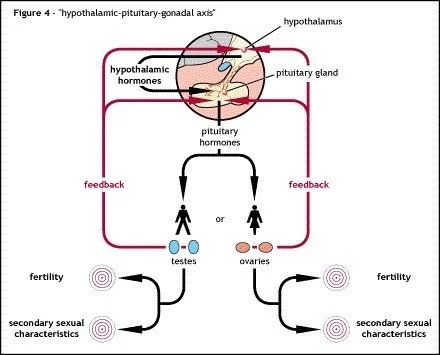
How is Kallmann syndrome / CHH diagnosed ?
There is no gold standard single test for Kallmann syndrome / congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (CHH).
Diagnosis is often made by excluding other possible conditions that could affect puberty or fertility
Standard blood tests would include:
Testosterone or oestrogen / progesterone
LH
FSH
Prolactin
SHBG
Vitamin D
Other tests could include:
MRI to examine the size and structure of the pituitary gland and check to see if olfactory bulb is present.
Smell identication test.
Wrist x-ray to determine bone age.
DEXA / DXA bone density scan.
Hearing test.
Neurological exam to check reflexes.
Genetic testing may be undertaken whch can help in some cases, especially if there is a family history of the condition but not all cases of Kallmann syndrome / CHH can be identified through genetics.