A
adrenal glands: a pair of endocrine glands located above the kidneys which produce small quantities of sex hormones, normally not affected in Kallmann syndrome
amenorrhoea: the failure of a woman to menstruate
ampoule: a small glass bottle containing a drug to be injected
anabolic: a type of steroid directed at muscle development
androgen: a type of male sex hormone, normally producing male secondary sexual characteristics
anosmia: a totally absent sense of smell
Aureliano Maestre de San Juan: Spanish doctor who in the 1850’s first described the condition that is now known as Kallmann syndrome
autosomes: those chromosomes which are not the sex chromosomes, (X or Y)
autosomal Kallmann syndrome: a form of inherited Kallmann syndrome which affects both men and women, because the sex chromosomes are unaffected
B
bimanual synkinesis: also known as mirror movements; the voluntary movement of one hand at the same time as involuntary movement of the other hand. Found in one particular form of Kallmann syndrome, called x-linked Kallmann syndrome
bone density measurement: procedure to measure strength of bones to test for osteoporosis or osteopenia
brittle bone disease: another term for osteoporosis
C
CT scan: computed tomography scan performed to visualise the pituitary and hypothalamus to check their shape and structure.
chromosomes: tiny thread-like packages which contain all the genetic information which make up a living being; almost every cell in the body, has an exact copy of 23 chromosome pairs, made up of 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes (X and / or Y)
cleft palate: a rare phenomenon which appears as a gap or crack in the roof of the mouth, sometimes seen in Kallmann syndrome patients
congenital: a disease or condition that is present from birth, such as Kallmann syndrome
constitutional delay in growth or puberty: sometimes referred to being a “late bloomer” or “late developer”, a condition where normal puberty is late starting.
cryptorchidism: a male defect which is characterised by a failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum just before or shortly after birth
D
DEXA scan: dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, used to test for bone strength (bone mineral density) in the diagnosis of osteoporosis or osteopenia
DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid. A double helix, highly complicated molecule that contains the information for formation and control of organsims. DNA forms itself into stuctures called genes, which are contained within the chromosomes of almost all living cells.
E
egg cell: the female sex cell, found in immature form within the ovaries
endocrine gland: an organ that releases a hormone directly into the blood stream
endocrinologist: a doctor who specialises in disorders of the endocrine / hormonal sysytems
endocrinology: the study of endocrine glands and hormones
endometrium: the active layer of the uterus, the thickness of which varies throughout the menstrual cycle
epiphyseal plates: those areas at the ends of the long bones which harden or fuse during normal puberty thus stopping further bone growth
ethinyloestradiol: a powerful derivation of the naturally occurring female sex hormone oestradiol (estradiol)
eunuchoidism (adj. eunuchoid): a characteristic of many hypogonadal men and women where the span from fingertip-to-fingertip exceeds their height; a eunuchoid who, unlike a eunuch, may still have relatively intact gonads, but his or her infertility and absent secondary sexual characteristics are the result of an hormonal imbalance rather than because of surgically removed gonads
F
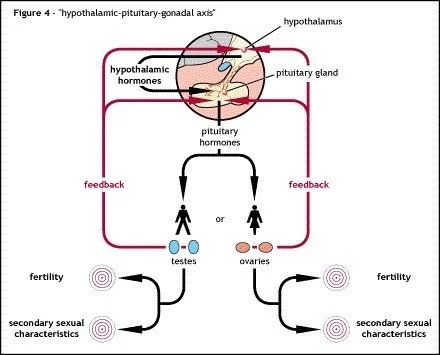
feedback system: a control mechanism used by many of the body’s systems to control (increase or decrease) the release of a particular hormone
fourth metacarpal: ring finger, sometimes shortened as symptom of having Kallmann syndrome
FSH: follicle stimulating hormone. A gonadotropin hormone, normally produced by the pituitary gland, helps to regulate the egg growth and release in females and sperm production in males. Abnormally low levels of FSH are found in patients with Kallmann syndrome
G
GH: Growth Hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland; one of the hormones responsible for normal bone development and teenage growth
gene (adj. genetic): a tiny unit containing a copy of a biological code which describes every one of our physical characteristics, such as the colour of our skin, eyes and hair but also the likelihood of us developing a particular disease; a gene is made up of segments of DNA
genome: the entire library of DNA information of an organism contained within its genes
GnRH: Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, secreted by the hypothalamus; GnRH stimulates the release of LH and FSH from the pituitary gland; the failure to secrete GnRH correctly is the fundamental cause of Kallmann syndrome
GnRH pulsatile therapy: a form of treatment which uses a portable, battery-driven pump to replace the missing GnRH by releasing it in pulses at regular intervals, typically every 90 minutes. Normally used for female fertility but can be used by male patients in some circumstances.
GnRH stimulation test: a hospital based test, normally lasting arounding 6 hours where the function of the hypothalamus is tested. Used to help to diagnose the cause of delayed or absent puberty
gonadotropin: hormones released by the pituitary gland under the influence of GnRH. The two gonoadotropins are called FSH and LH and are responsible for puberty and maintaining the reproductive cycle in both males and females. Abormally low levels of FSH and LH are seen in Kallmann syndrome
gonads: the sex endocrine glands, testes in men and ovaries in women
gynaecomastia: a usually harmless female-like enlargement of one or both breasts; a characteristic of some hypogonadal males caused by an inbalance of hormone levels
H
harelip: a clearly visible division of the upper lip, often appearing together with a cleft palate, sometimes seen in Kallmann syndrome patients
hCG: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; a hormone which behaves like LH; made by the placenta, hCG may be extracted or manufactured and used in the fertility treatment of both males and females. It can also be used to stimulate testosterone production in males.
hCG / hMG therapy: combined treatment that is often used in fertility treatment for both male and female Kallmann syndrome patients
hMG: Human Menopausal Gonadotropin; derived from the urine of post-menopausal women, hMG not only contains LH but also FSH. Used in fertility treatments.
hormone (adj. hormonal): a chemical messenger which is made and secreted by an endocrine gland and which targets one or more parts of the body, modifying its structure or changing the way it works
hormone replacment therapy: the name given to a form of treatment in which missing or deficient hormones can be replaced, the body being encouraged to behave normally as if it were making the hormones naturally
hypogonadism (adj. hypogonadal): the inability of the gonads (ovaries or testes) to function normally to release hormones and allow fertility
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: a very specific form of hypogonadism where the reason for the failure of the gonads is due to the abnormal (low) production of the the gonadotropins (LH and FSH) from the pituitary gland. Kallmann syndrome is a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. The condition is normally present from birth but can be aquired later in life after a normal puberty.
hyposmia (adj. hyposmic): partial sense of smell
hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis: the name given to the team of glands that together control puberty and fertility (hypothalamus / pituitary / gonads)
hypothalamus: a thumbnail-sized endocrine gland located in the brain just above the pituitary gland to which it is connected; the hypothalamus normally contains cells which make and release GnRH, but in Kallmann syndrome, there are very few (if any) of these cells present. The hypothalmus controls many of the body’s functions such as body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep and sex drive.
I
idiopathic: a term used to describe a disease with an unknown cause or origin
infertility (adj. infertile): the inability to conceive or to induce conception; a characteristic of the untreated Kallmann syndrome patient
inheritance (v. to inherit): the passing on of a gene from generation to generation, from one or both of the parents
intramuscular injection: an injection which is given deep into the muscle, such as the buttocks or thigh
K
Kallmann syndrome: a specific form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism that is also associated with and absent or severly reduced sense of smell
Kallmann, Franz J: the New York psychiatrist and geneticist who, in 1944 was the first to offer a genetic explanation for a medical condition observed in some of his patients who were both sexually immature and anosmic
karyotype: blood test to determine the number of chromosomes within a cell; used in the diagnosis of chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome or Turner syndrome
kisspeptin: a hormone that controls puberty and fertility by affecting GnRH release by the hypothalamus; has potential to be used as a treatment for some types of infertility or in the early diagnosis of Kallmann syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome: also known as 47 XXY, chromosomal disorder that can in some cases cause low testosterone levels and infertility
L
Leydig (interstitial) cells: special cells in the testes where around 95% of the male sex hormone testosterone is made; the remaining 5% is made by the adrenal glands
LH: luteinizing hormone; a gonadotrophin secreted by the pituitary gland, the hormone promotes ovulation / egg release in females and testosterone production in males
LHRH: luteinizing hormone releasing hormone; another name for GnRH
M
MRI scan: magnetic resonance imaging scan; similar to a CT scan but does not use potentially harmful X-rays to be able to see structures within the brain to help in diagnosis
medroxyprogesterone actetate: a semi-synthetic medication which is close in structure and function to the naturally occuring female sex hormone, progesterone
menopause (adj. menopausal): that time of an adult woman:s life during which she no longer menstruates, usually between the ages of 45 and 55
menstrual cycle: a monthly cycle experienced by nonpregnant women during which physical changes to her uterus (more specifically her endometrium) take place due to varying hormone levels in preparation for the potential reception of a fertilised egg cell
menstruation (v. to menstruate): the monthly bleeding at the beginning of the menstrual cycle, caused by the shedding of the endometrium in the event of no fertilised egg cell becoming implanted
microphallus: the name given to very small genitalia, usually the penis
mirror movements: see bimanual synkinesis
mutation (v. to mutate): a change in the structure of the DNA molecule, causing a change in the genetic information carried by it; not all mutations are harmful or cause any significant change in an organism
N
nasal cavity: the space in the nose which lies just above the roof of the mouth and which houses members of the olfactory system
neuron: a nerve cell
NGS: next generation sequencing, a modern type of genetic testing where the entire genome is identified instead of looking for specific genes
O
oestradiol: one of the three female sex hormones manufactured and secreted by the ovaries; the others being oestrone and oestriol which are produced elsewhere in the body
oestrogen: the primary female sex hormone produced by the ovaries, responsible, among other things, for the female secondary sexual characteristics; also made in small quantities by the males
olfactory cells: specialised cells found at the top of the nasal cavity which converts a smell detected by the olfactory hairs into tiny electrical signals
olfactory bulb: one of two structures connected to the olfactory tracts to which the olfactory cells are anchored
olfactory hairs: nerve fibres which detect a smell once it enters the nasal cavity
olfactory system: the name given to the group of olfactory organs and structures, such as the olfactory hairs, cells, bulbs and tracts
olfactory tract: one of two structures containing neurons which carry the smell from the olfactory cells, where it has been converted into an electrical signal, to the area of the brain where the smell can be identified
orchidometer: medical device, comprising of a series of plastic or wooden beads used by doctors to estimate testicle size
orchidopexy: the surgical procedure used to correct cryptorchidism; undescended testes are brought down into the scrotum
osteoporosis (adj. osteoporotic): a condition characterised by weakened and brittle bones, arising from an hormonal imbalance; also known as brittle bone disease
ovary (pl. ovaries) ovulation (v. to ovulate): the female gonad; site of production of egg cells and sex hormones; the release of an egg cell from the ovary, about halfway through the menstrual cycle, ready for fertilisation by a sperm cell
P
pituitary gland: a pea-sized endocrine gland, linked to and located just under the hypothalamus; source of the gonadotropins LH and FSH
pituitary stalk: a tiny structure which connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland
placenta: the organ which contains, protects and nourishes a developing baby in the uterus
primary amenorrhoea: the inability to menstruate, caused by a failure of sexual maturation and function
primary sexual characteristics: the group of physical characteristics which is directly involved in sexual reproduction, such as the penis and testes in men and the vagina and ovaries in women
progesterone: a sex hormone which is made in the ovaries and during pregnancy, by the placenta as well; helps to build up the endometrium during the menstrual cycle
puberty (adj. pubertal): the period during which the secondary sexual characteristics become apparent and the person becomes capable of sexual reproduction; boys generally reach puberty by the time they are 16, girls a year or two earlier
S
scoliosis: abnormal curvature of the spine, seen in some Kallmann syndrome patients
scrotum: a skin-covered pouch which holds the testes and attached structures
secondary sexual characteristics: the group of physical characteristics which are not directly related to sexual reproduction; these include the growth of pubic and body hair, the breaking of a boy’s voice, the growth of the female breasts, muscle growth and fat distribution
secretion (v. to secrete): the process by which an endocrine gland releases a hormone or hormones it has produced
sex cell: one of the cells produced in the testes (sperm cells) or the ovaries (egg cells); a sex cell contains 22 unpaired autosomes and one unpaired sex chromosome
sex chromosome: one of the 23rd pair of chromosomes; a male has one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, a woman has two X chromosomes
sex hormone: any of one of a group of hormones made by the gonads, including the male hormone testosterone and the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone
sperm cell spermatogenesis: the process of sperm cell production in the testes, stimulated by testosterone and FSH; takes about 76 days to be completed from beginning to end
subcutaneous mastectomy: an operation carried out to correct gynaecomastia; the enlarged tissue under the skin of the breast is removed, often leaving a small scar around the nipple area
T
TESE: testicular sperm extraction, can be used as part of male fertility treatments or in the diagnosis of low sperm counts
testis (pl. testes): the male gonad; site of production of testosterone and spermatogenesis
testosterone: the main male sex hormone, its production encouraged by LH from the pituitary gland; small amounts also present in women
U
ultrasound: a commonly used diagnostic technique which uses sound waves to see inside the body; often used on pregnant women to monitor the growth of unborn babies, but also helps to detect unilateral renal agenesis and testicle size
undecanoate: a form of testosterone that is often used in male HRT products, containing a balance of androgenic and anabolic properties.
unilateral renal agenesis: a rare characteristic of some patients with x-linked Kallmann syndrome; one of the two kidneys is either completely absent or only partially formed
uterus: the organ which houses the embryo and unborn baby during its development; its lining is called the endometrium
W
womb: another term for the uterus
wrist x-ray: imaging test used to determine the chronological age of a person’s bones, used in the diagnosis of delayed puberty
X
X chromosome: one of the sex related chromosomes
X-linked: a term used to describe a defective gene which is located on or linked to the X chromosome; normally only men develop a disease as a result, women can only be carriers or in some cases carry a milder version of the disease
Y
Y chromosome: the other sex chromosome; paired with an X chromosome, the Y chromosome means that the sex is male; women have no Y chromosomes